Comprehensive Guide to Nutrition & Feeding in Pigeon Rescue
Proper nutrition is a cornerstone of successful pigeon rescue and rehabilitation. Understanding the fundamental basics and essential knowledge of pigeon diet and feeding practices ensures rescued pigeons recover well and maintain optimal health. This guide synthesizes current expert recommendations and practical feeding strategies tailored for rescuers and caregivers.
Why Nutrition Matters in Pigeon Rescue
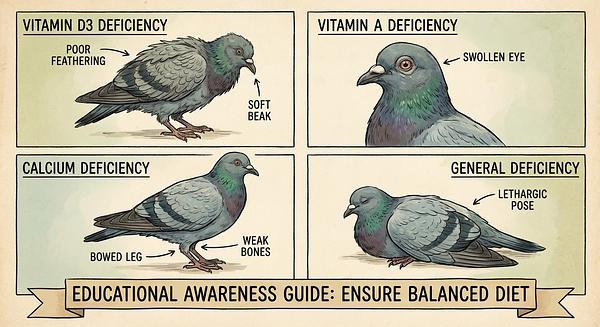
Pigeons require a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, protein, and appropriate fats to support feather regrowth, immune function, and overall vitality. Incomplete or poor diets—such as feeding bread, only seeds, or high-fat grains—can lead to serious health issues including poor feather quality, respiratory infections, fatty liver, and metabolic disorders like diabetes.
Fundamental Nutritional Components for Pigeons
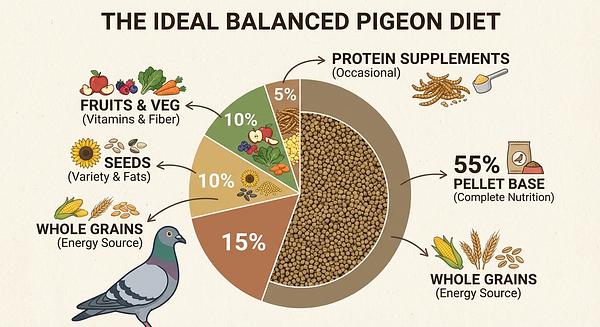
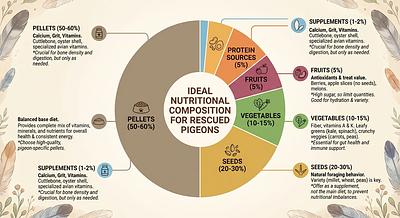
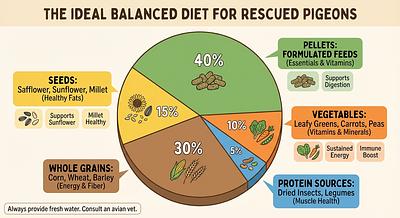
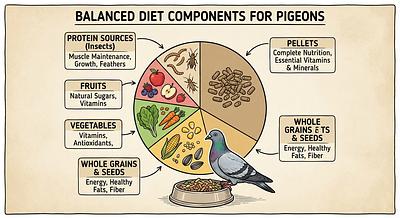
1. Balanced Base Diet
- Pellets or Crumbles formulated for pigeons: These are recommended as the primary food source because they are low in fat but high in essential vitamins and minerals. Brands like APC Pigeon Pellets or Passwell Crumbles provide a nutritionally complete base.
- Whole grains and seeds: A complementary mix including wheat, maize, peas, safflower, sorghum, and corn can be offered alongside pellets. A good basic mix might be 40% peas, 15% safflower, 15% wheat, 15% sorghum, and 15% maize.
- Small seeds as treats: Finches or canary seeds can be given sparingly to enrich the diet.
2. Fresh Fruits and Vegetables
- Pigeons benefit from fresh produce such as peas, corn, carrots, berries, leafy greens like kale and dandelion, broccoli, snap peas, and bell peppers.
- Avoid toxic foods: Never feed avocado, onion, or rhubarb, as these are harmful to pigeons.
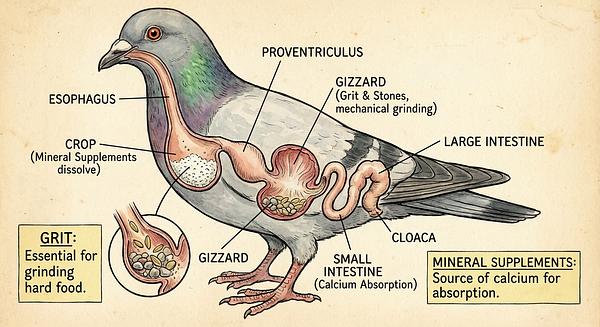
3. Grit and Mineral Supplements
- Grit: Composed of crushed shells and stones, grit helps digestion and provides trace minerals.
- Mineral blocks: Red pigeon grit and crushed oyster shell (used sparingly as seasoning) supply calcium and other minerals vital for bone and eggshell health.
4. Protein Enrichment
- Pigeons naturally forage insects and worms. Supplementing with mealworms, crickets, earthworms, or wood roaches provides additional protein, crucial especially during rehabilitation phases.
5. Vitamins and Specialty Supplements
- A multivitamin/multimineral supplement containing calcium and vitamin D3 is important, particularly for indoor or limited sun-exposed birds to prevent deficiencies.
- Garlic supplements (garlic oil or juice) can promote feather and digestive health and boost immunity when added periodically to food or water.
6. Hydration
- Fresh, clean water must always be available and changed daily.
- For dehydrated or weak pigeons, electrolyte solutions (a small pinch of salt and sugar dissolved in water) can aid recovery.
Feeding Guidelines and Practical Tips
Offer Variety and Balance
- Aim for 50%-100% pellets as the diet base.
- Supplement with whole grains, seeds, fresh fruits, and vegetables for diversity and enrichment.
- Use proteins and treats sparingly and thoughtfully to avoid excessive fat intake.
Feeding for Rescued and Weak Pigeons
- Start with gentle hydration techniques, encouraging drinking by dipping the beak gently into water.
- For pigeons not eating, offer thawed frozen peas warmed in water as a safe hand-feeding option to restart digestion.
- Avoid sudden large feedings to prevent crop issues; feed small amounts frequently as needed.
Feeding Equipment and Environment
- Use shallow, heavy dishes to prevent tipping and contamination.
- Place food bowls where pigeons won’t perch on them to avoid soiling the food.
- Provide multiple flat surfaces for perching away from the food bowls.
Monitoring Intake
- Adjust feeding amounts so that food offered in the morning is consumed by evening to minimize spoilage.
- For baby pigeons, feed until the crop feels soft and squishy like a 3/4 full water balloon, ensuring they are neither under- nor overfed.
Specialized Considerations
Egg-Laying Females
- Provide additional calcium via liquid supplements in water to support eggshell formation.
Vitamin D3 and Lighting
- Use a full-spectrum light bulb to aid vitamin D metabolism, especially for indoor birds lacking natural sunlight exposure.
Avoid Harmful Foods
- Do not feed bread, milk, oatmeal, or any human junk food.
- Avoid high-salt or inappropriate grit products (e.g., chicken oyster shell grit or high-salt grit).
Summary
Successful pigeon rescue nutrition relies on a balanced, varied diet emphasizing formulated pellets, whole grains, fresh produce, and protein supplementation, alongside proper hydration and mineral support. Careful feeding practices tailored to the bird’s condition and stage of recovery improve health outcomes and promote longevity. Regular monitoring and adjustment ensure pigeons receive all essential nutrients without the risks posed by incomplete or inappropriate diets.
References:
- Melbourne Bird Veterinary Clinic
- Palomacy Rescue Guidelines
- Great Lakes Pigeon Rescue
- Merck Veterinary Manual on Orphaned Birds
- Pigeon and Dove Rescue UK



💬 Comments (0)