Advanced Nutrition & Feeding Practices in Pigeon Rescue
Proper nutrition is fundamental to the successful rescue, rehabilitation, and long-term care of pigeons. While basic feeding guidelines emphasize seeds and grains, advanced care requires a nuanced understanding of dietary balance, supplementation, feeding techniques, and hydration strategies to support recovery and optimal health.
Understanding Pigeon Dietary Needs
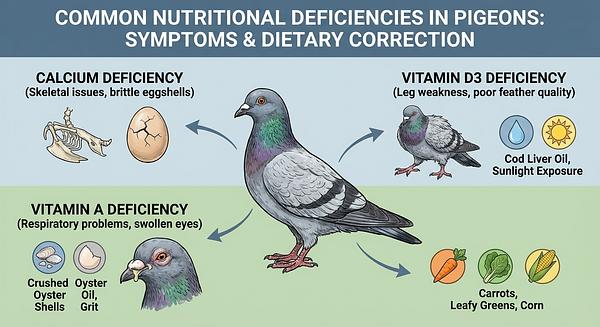
Pigeons are primarily granivores, naturally consuming a variety of seeds and grains. However, a diet based solely on seeds is often deficient in essential nutrients such as calcium, vitamin A, and vitamin D3, which are critical for bone health, immune function, and overall vitality.
Key Nutritional Components:
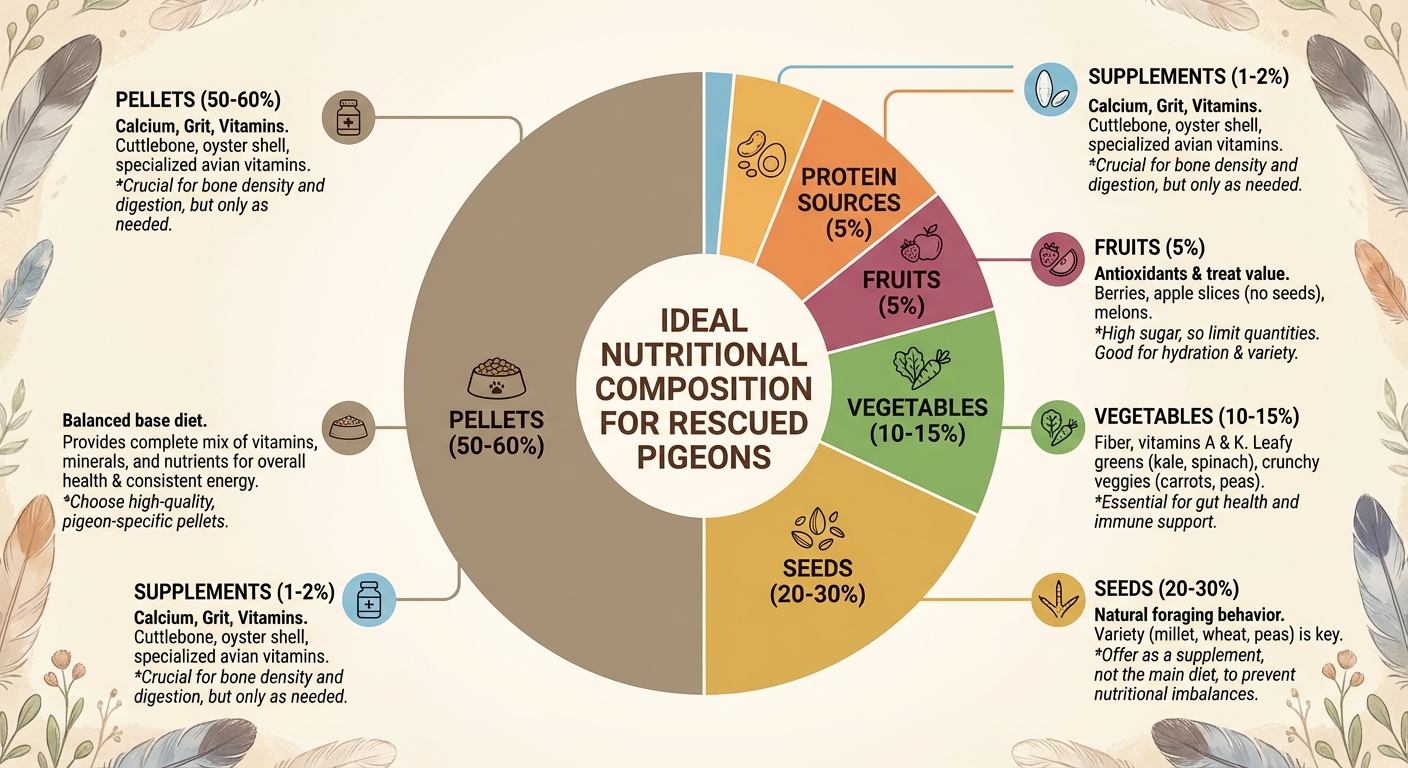
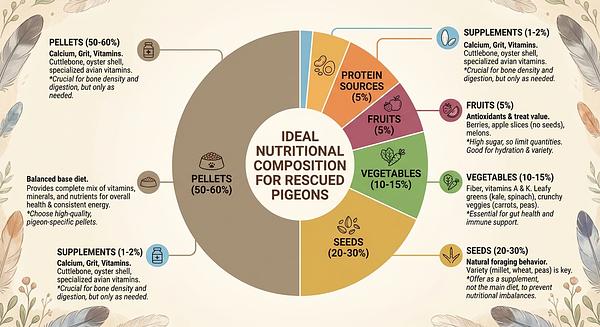
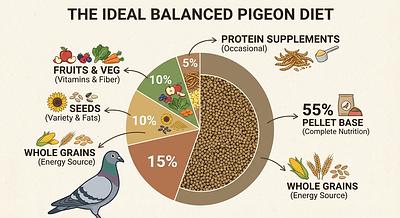
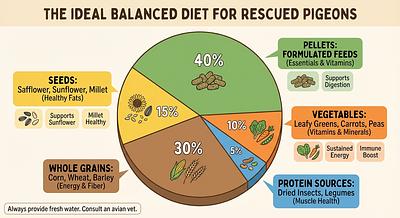
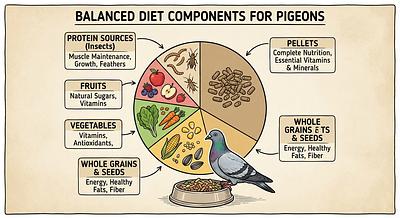
Balanced Pelleted Diets: High-quality formulated pelleted diets (e.g., Harrison’s Bird Diet) should constitute approximately 50% of the diet. These are designed to provide balanced nutrition and prevent selective feeding on only favorite seeds.
Seeds and Grains: While seeds remain important, they should be part of a mixed diet and not exceed 30-40%. Avoid all-seed diets to prevent nutrient imbalances and obesity.
Vegetables and Greens: Fresh vegetables, especially dark leafy greens such as kale, dandelion, and broccoli, should be offered regularly (3-4 times per week). These supply vitamins, minerals, and fiber essential for digestive and immune health.
Fruits: Offered sparingly (about 5% of diet) due to high sugar content. Fresh berries, papaya, and mango are beneficial, but they should not remain in the cage for long to prevent fermentation.
Protein Supplements: Cooked legumes, eggs, tofu, and whole grain breads provide additional protein, which is valuable especially during recovery phases.
Calcium and Grit: Supplementation with bird-safe grit and crushed oyster shell (used sparingly) supports digestion and calcium needs, particularly for egg-laying females. Avoid grit high in salt or inappropriate for pigeons.
Vitamin D3 and Sunlight: Exposure to natural sunlight or full-spectrum lighting is crucial for vitamin D metabolism, supporting calcium absorption and bone health.
Feeding Techniques for Rescued or Sick Pigeons
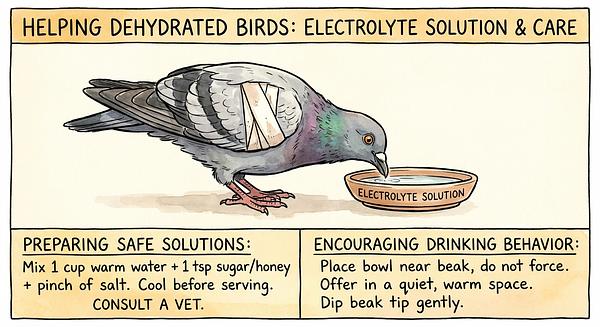
Hydration First
Dehydration is common in rescued pigeons and must be addressed before nutritional rehabilitation. Offer plain water immediately; if the bird is weak, provide an electrolyte solution by dissolving a pinch of salt and sugar in water. For birds reluctant to drink, gently dip the beak tip in water to encourage hydration.
Gradual Refeeding
Avoid Overfeeding: Starved birds are at risk of refeeding syndrome. Start with small, frequent feedings of easily digestible foods like thawed frozen peas before advancing to regular diets.
Hand Feeding: When necessary, use gentle hand-feeding of warm, moistened foods via syringe or crop feeding tube. Positioning the feeding tube carefully minimizes stress and injury. Use formulas such as Harrison's Recovery Formula for critical cases.
Meal Feeding
Pigeons do best with meal feeding: provide a fresh, appropriate portion of food in the morning, ensuring it is consumed by evening. This prevents overeating of high-fat seeds and reduces waste.
Start with about 2 tablespoons per bird and adjust based on consumption and body condition.
Supplementation
Multivitamins & Minerals: Incorporate a high-quality avian vitamin/mineral supplement into the food to ensure full nutritional coverage, particularly calcium and vitamin D3.
Garlic Supplement: Adding garlic juice or oil weekly supports feather quality, digestive health, and immune function.
Liquid Calcium: For egg-laying females, adding liquid calcium supplements to drinking water is important to prevent deficiencies.
Practical Tips for Caregivers
Food Presentation: Use shallow, heavy dishes to prevent tipping. Clean food and water dishes daily to prevent bacterial contamination.
Safe Foods Only: Avoid toxic foods like avocado and iceberg lettuce. Favor nutrient-dense vegetables and fruits.
Monitor Intake: Track daily food and water consumption per bird to adjust diet and detect health issues early.
Avoid Microwaving: Heat foods by warm water baths to prevent hot spots that could injure the bird’s crop or mouth.
Environmental Lighting: Use full-spectrum light bulbs in indoor aviaries to simulate natural sunlight for vitamin D synthesis.
Advanced Nutritional Strategies
Intestinal Health: Probiotic-rich foods or supplements may aid gut flora balance, enhancing nutrient absorption and immunity.
Customized Diets: Adjust nutrient ratios based on age, health status, breeding, or recovery to optimize outcomes.
Emergency Feeding Protocols: In severely debilitated pigeons, use specialized recovery formulas and controlled feeding volumes guided by avian veterinarians to reduce mortality risk.
By applying these advanced nutrition and feeding practices, rescuers and caregivers can significantly improve the health, recovery, and longevity of pigeons in their care, moving beyond basic feeding to holistic, evidence-based avian nutrition management.

💬 Comments (0)