Pigeon Rescue: Comprehensive Guide to Pigeon Health & Medicine
Rescuing and caring for pigeons involves more than just providing shelter and food; it requires a thorough understanding of common health challenges and effective medical treatments. This article delves into the most prevalent diseases affecting pigeons, their symptoms, prevention methods, and treatment options, focusing on practical advice for rescuers and caregivers dedicated to improving pigeon welfare.
Common Health Challenges in Pigeons
Pigeons are susceptible to a variety of infectious diseases and parasitic infestations that can severely affect their health, performance, and survival. The most frequent health issues include:
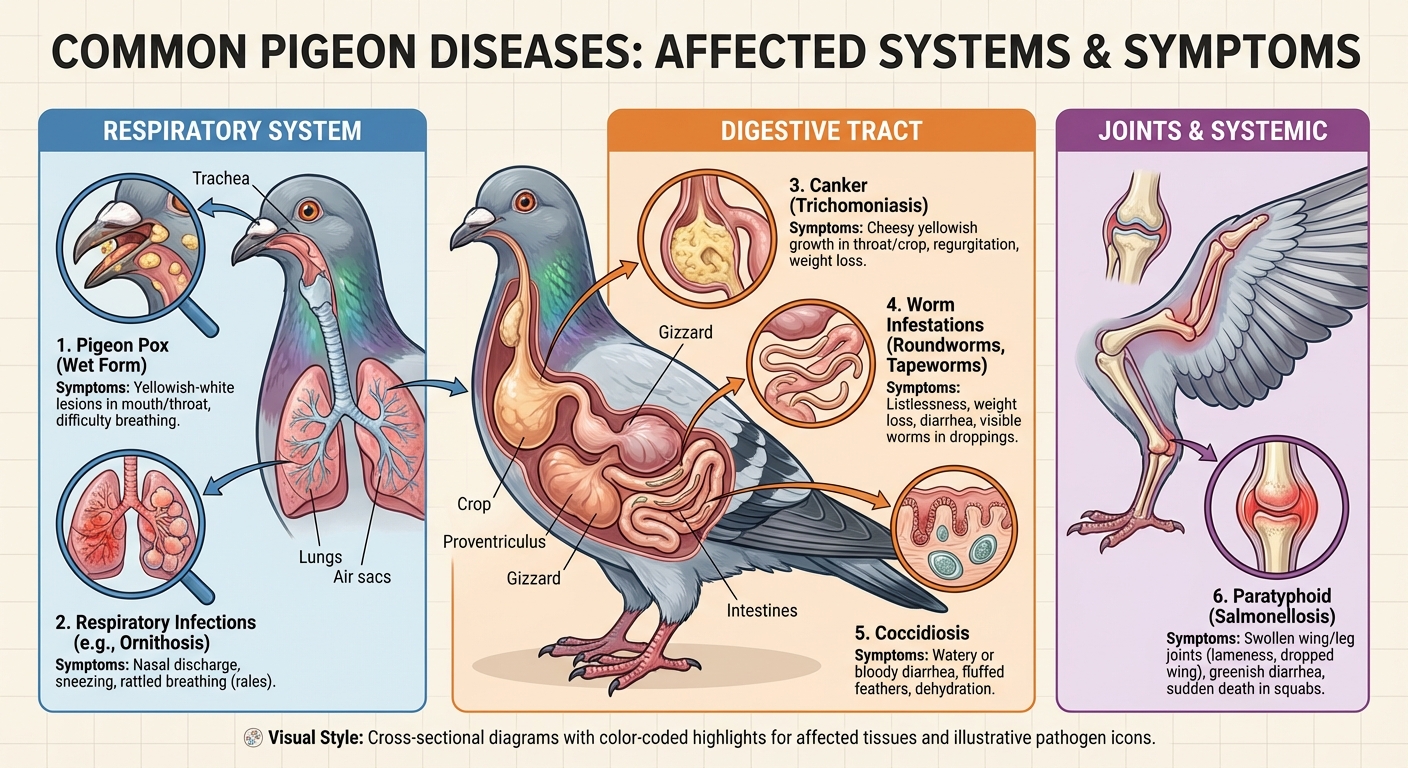
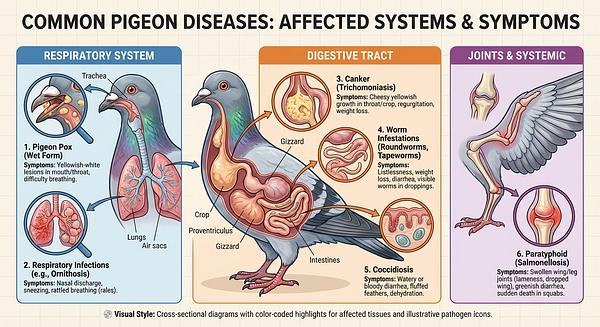
1. Paramyxovirus (PMV)
- Description: A viral disease causing neurological symptoms such as tremors, twisting of the neck, and paralysis.
- Challenges: Once infected, pigeons become carriers for life; vaccination does not cure but prevents infection.
- Management: Vaccination is critical for prevention. Infected birds can be treated with La-Sota vaccine applied individually (eye drops for 3 consecutive days) or added to drinking water for flock treatment. Isolation after treatment is important to prevent spread.
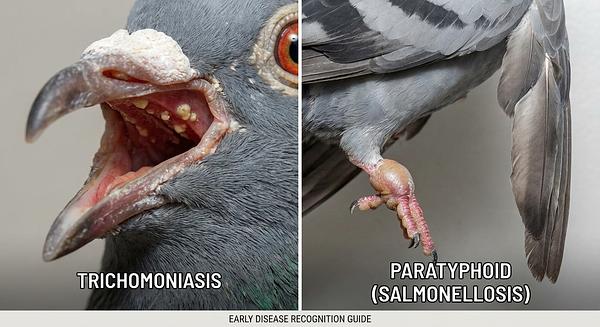
2. Paratyphoid (Salmonella infection)
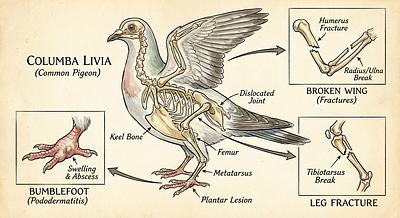
- Description: A bacterial disease leading to sudden deaths, diarrhea, swollen joints, dropped wings, infertility, and weight loss.
- Challenges: Difficult to eradicate due to environmental persistence and rodent carriers.
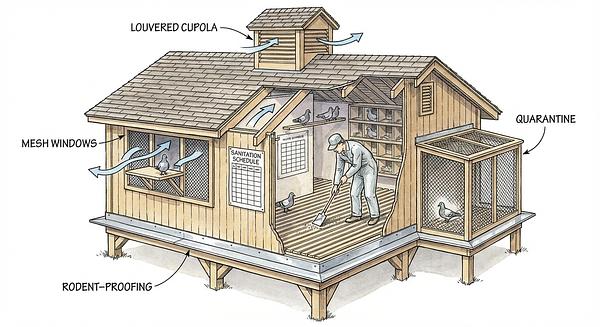
- Prevention: Maintain strict loft hygiene, control rodents, and quarantine new birds for at least 5 days before introducing them.
- Treatment: Antibiotics such as fluoroquinolones (Baytril, Cipro) for 10-14 days; vaccination is recommended in lofts with previous infections.
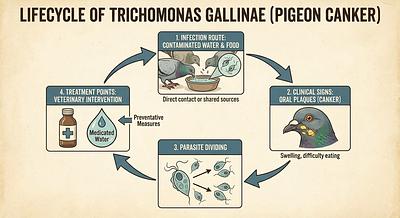
3. Trichomoniasis (Canker)
- Description: Caused by the parasite Trichomonas gallinae, characterized by yellow lesions in the oral cavity.
- Challenges: Common and often co-occurs with other infections; untreated cases can be fatal.
- Treatment: Use specific anti-protozoals such as Ronidazole, Tricho Cure+, or Emtryl, administered in water or individually. Treat co-infections simultaneously.
4. Respiratory Infections (Ornithosis Complex, Mycoplasmosis)
- Description: Includes bacterial, viral, and parasitic pathogens causing sneezing, nasal discharge, and breathing difficulties.
- Challenges: Secondary infections often complicate respiratory diseases.
- Treatment: Antibiotics like doxycycline and natural supportive supplements such as Respi Green to maintain airways mucus-free. Environmental management is crucial to prevent recurrence.
5. Blood Parasites (Haemoproteus)
- Description: Spread by pigeon flies, causing anemia and weakened condition.
- Management: Control of pigeon flies plus preventative treatment with Atabrine before and during racing season.
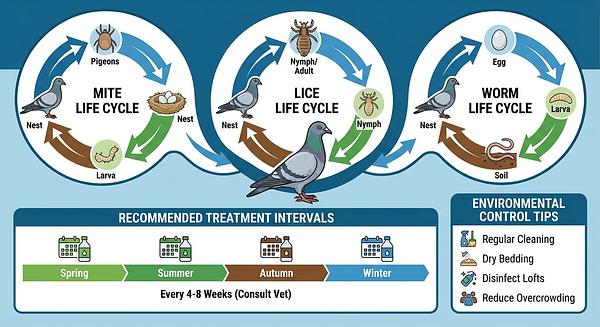
6. Parasites (Worms, Mites, Lice)
- Description: Internal and external parasites cause poor condition, feather damage, and disease susceptibility.
- Treatment: Ivermectin for internal parasites; regular dusting or spraying for external parasites. Environmental sanitation to reduce parasite habitats is essential.
7. Pigeon Pox
- Description: Viral disease causing lesions on the skin and mucous membranes.
- Prevention: Vaccination is the only effective protection.
- Management: Provide supportive care during outbreaks.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Pigeon Health & Medicine
Maintaining Good Immunity
- Vaccination Programs: Essential for prevention of Paramyxovirus, Pigeon Pox, and Paratyphoid.
- Nutrition & Supplements: Use products like Healthy Oil, Vit Amino, and Protein Plus to boost immunity and support recovery.
Hygiene and Loft Management
- Daily cleaning and disinfection reduce pathogen load.
- Rodent and insect control prevents disease transmission.
- Quarantine new or sick birds to avoid spreading infections.
Medication Protocols
- Administer treatments as per veterinary guidance, tailored to disease severity.
- Use combination therapies when co-infections are suspected.
- Monitor response and adjust treatment duration accordingly.
Integrated Health Approach
- Combine vaccination, medication, nutritional support, and environmental management.
- Regular health checks and fecal exams to detect parasites early.
- Proactive parasite control reduces stress and improves performance.
Handling Treatment Difficulties
- Some diseases, like Paramyxovirus, have no cure, making prevention paramount.
- Paratyphoid treatment may require loft-wide remediation, including euthanasia of severely affected pigeons and repeated disinfection.
- Antibiotic resistance considerations necessitate sensitivity testing before treatment.
Practical Advice for Rescuers and Caregivers
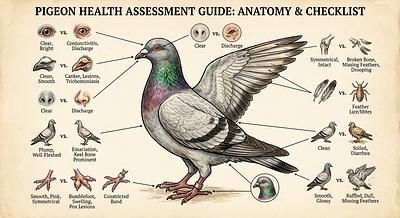
- Observe closely: Early detection of symptoms is key to successful treatment.
- Consult avian veterinarians: Use professional advice for vaccination schedules and drug choices.
- Use approved medications: Ensure dosage and administration follow veterinary recommendations.
- Keep detailed records: Track treatments, vaccinations, and outcomes.
- Create a safe environment: Provide clean water, balanced nutrition, and minimize stress.
Pigeon rescue is a rewarding but demanding endeavor requiring knowledge and vigilance regarding health challenges. By understanding common diseases, embracing preventative strategies, and applying appropriate medical treatments, rescuers can significantly improve the survival and quality of life for these resilient birds.
💬 Comments (0)