Comprehensive Guide to Habitat & Housing for Rescued Pigeons
Creating a safe, comfortable, and enriching habitat is essential for the well-being and rehabilitation of rescued pigeons. Whether you are housing pigeons indoors or outdoors, following a detailed, step-by-step approach ensures the birds thrive physically and emotionally. This guide provides practical instructions for rescuers and caregivers, focusing on building appropriate housing, maintaining hygiene, and enriching the environment.
1. Understanding Pigeon Habitat Needs
Pigeons are social, ground-feeding birds that require space to fly, perch, forage, and bathe. Their housing must protect them from predators and harsh weather while providing mental stimulation and social interaction.
Key habitat requirements:
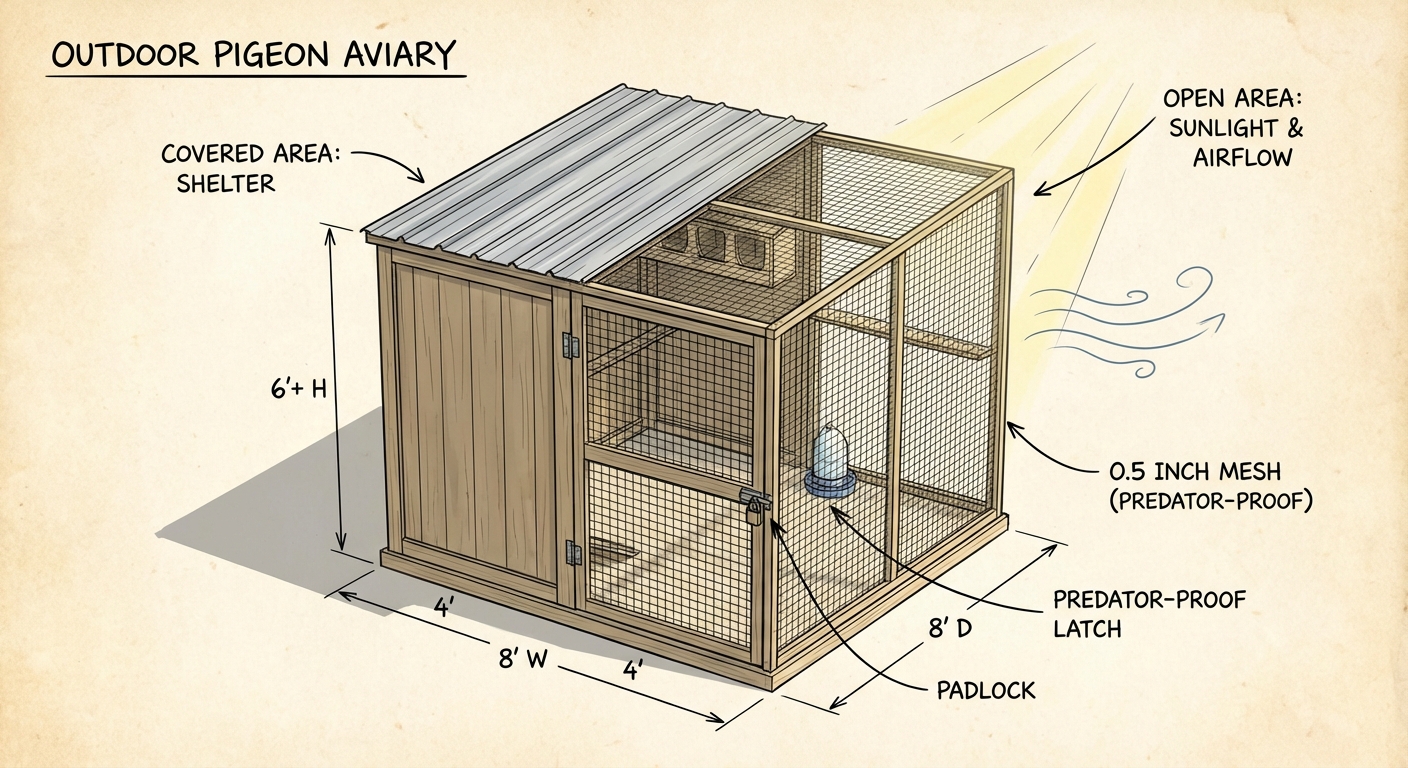
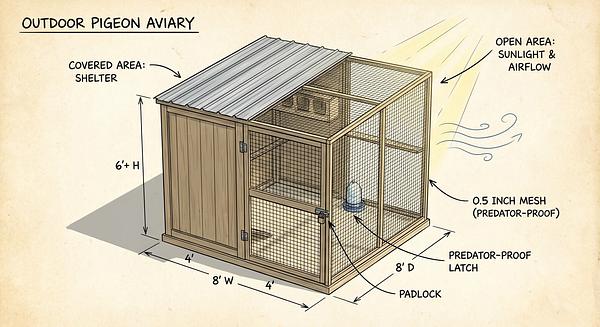
- Space: Minimum recommended aviary size is 4' wide x 6' long x 6' high for outdoor pigeons; indoor cages should be at least 36" wide for one or two birds.
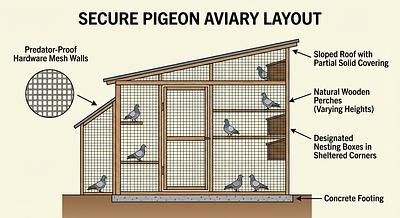
- Safety: Predator-proof construction with sturdy mesh (maximum 0.5" openings) and secure latches.
- Shelter: Half of the aviary should be sheltered from rain, wind, and extreme sun.
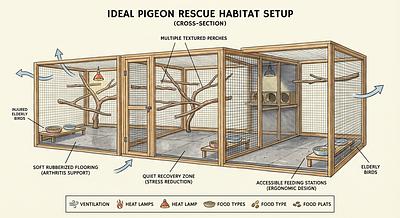
- Perches and Shelves: Multiple perches and shelves at varying heights to allow natural behaviors.
- Bathing Facilities: Large, shallow dishes for water baths.
- Diet and Foraging: Access to fresh food and water daily, with solid flooring and litter to allow for natural foraging.
2. Step-by-Step Guide to Setting Up Indoor Housing
Step 1: Select an Appropriate Cage
- Choose a cage with a minimum width of 36" for one or two pigeons.
- Avoid wire grid floors; opt for solid bottoms lined with suitable litter (e.g., paper or wood shavings) to enable foraging.
- Include flat-bottom ceramic dishes for food and water to prevent tipping.
Step 2: Provide Environmental Enrichment
- Install shelves instead of simple perches; pigeons lounge better on flat surfaces.
- Place a large mirror inside the cage, as pigeons recognize themselves and enjoy visual companionship.
- Include a weighted basket or nest box with replaceable nesting material like pine needles.
- Add toys or small treat holders to stimulate natural behaviors.
Step 3: Ensure Proper Lighting and Airflow
- Position the cage near a window with unfiltered sunlight or use avian-safe full-spectrum lighting.
- Maintain good ventilation but avoid drafts.
Step 4: Daily Care and Interaction
- Provide supervised out-of-cage time indoors for exercise.
- Include bathing opportunities daily with a shallow water dish.
- Spend time with the birds or provide another pigeon companion to prevent loneliness.
3. Step-by-Step Guide to Building an Outdoor Aviary
Step 1: Choose the Location
- Select a sunny spot with balance for shade and rain shelter.
- Ensure the area is quiet enough to reduce stress but visible for easy monitoring.
Step 2: Construct the Aviary Frame and Mesh
- Build a sturdy frame using wood or metal.
- Use hardware cloth or welded wire mesh with openings no larger than 0.5" to be predator and rodent-proof.
- Avoid chicken wire or bird netting as they can entangle birds.
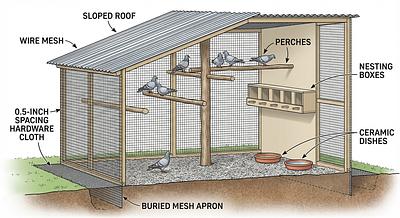
Step 3: Add Flooring and Shelter
- Provide a solid floor covered with litter to allow foraging.
- Half the aviary should have a roof and siding to protect from weather.
- Use sloped or peaked roofing to prevent water pooling.
Step 4: Install Perches and Nest Boxes
- Use natural branches (1-2" diameter) for varied grip and comfort.
- Place perches at multiple heights and near mesh walls for bird viewing.
- Provide at least one nest box per breeding pair, filled with natural nesting materials.
Step 5: Provide Food, Water, and Bathing Facilities
- Use flat-bottom ceramic dishes for food and water, refreshed daily.
- Include a large shallow pan for bathing.
Step 6: Secure Doors and Latches
- Use raccoon-proof latches and ensure all access points are tightly secured.
4. Maintenance and Health Considerations
- Clean food and water dishes daily.
- Remove feces and replace bedding regularly to maintain hygiene and reduce dust.
- Monitor birds for signs of illness; provide veterinary care promptly.
- Avoid overcrowding; allow at least 32 cubic feet per pigeon in aviaries to reduce stress.
5. Additional Tips for Enriching Pigeon Habitats
- Rotate toys and nesting materials to keep the environment interesting.
- Provide opportunities for social interaction, as pigeons are highly social.
- Use natural sunlight and fresh air exposure to support health.
- Avoid free outdoor flight unless in a secure aviary or harness to protect from predators.
Creating a well-designed habitat combining safety, space, enrichment, and proper care significantly enhances the welfare of rescued pigeons and supports their rehabilitation and successful adoption.



💬 Comments (0)