Advanced Techniques and Best Practices in Pigeon Rescue & Rehabilitation
Pigeon rescue and rehabilitation require a combination of careful capture methods, immediate supportive care, and long-term rehabilitation strategies tailored to the species’ unique physiology and behavior. This comprehensive guide covers advanced rescue techniques and rehabilitation best practices that go beyond basic introductory knowledge, aimed at rescuers and caregivers who want to optimize outcomes for rescued pigeons.
Safe and Effective Rescue Techniques
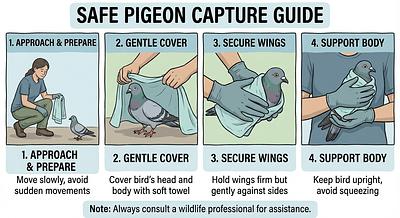
1. Assessing the Situation and Preparing
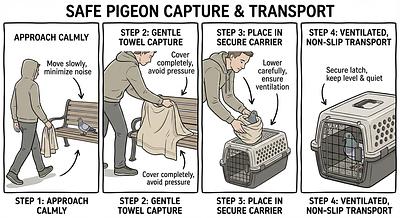
- Environment: Approach the pigeon calmly to avoid stress or injury. Evaluate surroundings for hazards like traffic or predators.
- Equipment: Use appropriate tools such as fine-mesh nets, towels, or crate-and-string traps to safely capture the bird without harm.
2. Capture Methods
Hand Capture with Minimal Stress
- For tame or weak pigeons, gently scoop them up with both hands, ensuring wings are held against the body to prevent flapping and injury.
- If the pigeon tries to escape but is weak, guide it gently into a corner or open door, then cover it quickly with a towel or sweater before lifting.
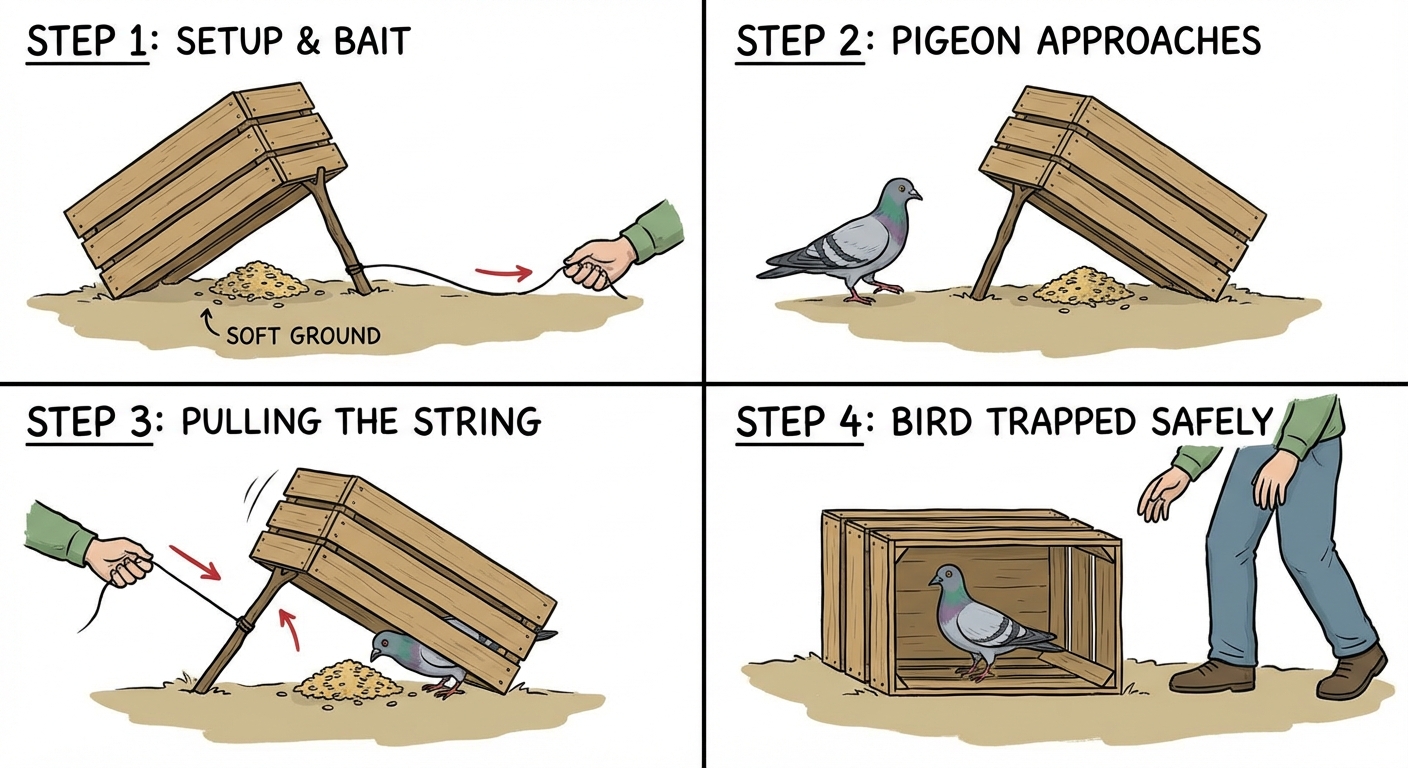
Crate-and-String Trap
- Use a medium box or laundry basket propped with a stick and bait it with food and water.
- Attach a string to the stick so that when the bird moves under the box for food, pulling the string closes the box safely trapping the pigeon without injury.
Wile E. Coyote Box Trap
- Similar to the crate trap but often used in dim lighting to reduce bird’s visual cues for escape.
- Cover yourself and the box with a blanket to safely capture the pigeon once trapped.
Direct Pinning Technique
- Scatter food in a line to attract pigeons.
- Slowly approach the targeted pigeon, then swiftly pin it to the ground with an open hand, forming a basket around the bird without applying harmful pressure.
- Practice this technique for smooth execution and to prevent injury to both rescuer and bird.
3. Handling After Capture
- Immediately place the pigeon in a ventilated container lined with paper or soft material.
- Keep the container in a warm, quiet, low-light environment away from pets and human traffic.
- Provide a heat source such as a wrapped hot water bottle or microwaveable rice sock to help maintain body temperature.
Advanced Rehabilitation Protocols
1. Initial Assessment and Stabilization
- Physical Examination: Check for wounds, bleeding, deformities, or signs of infection.
- Hydration and Nutrition: Administer rehydrating fluids orally or subcutaneously if trained, as dehydration is common in injured or stressed pigeons.
- Offer easily digestible feed such as specialized pigeon pellets or soaked grains.
2. Medical Care
- Wound Management: Clean wounds with saline, apply antiseptic as appropriate, and use bandages or splints for fractures.
- Medication: Administer antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, or pain relief under veterinary guidance.
- Parasite Control: Check for external parasites like mites and treat accordingly.
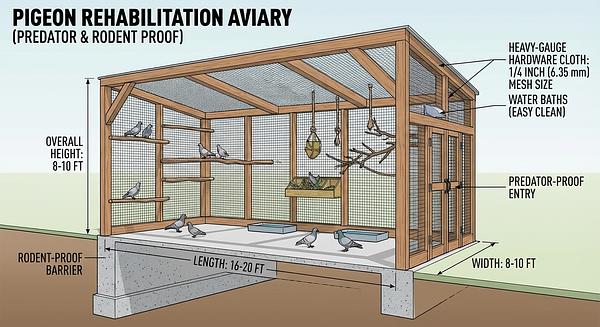
3. Housing and Environmental Enrichment
- Use predator- and rodent-proof aviaries made with hardware cloth (mesh opening no larger than 0.5 inches), avoiding chicken wire.
- Aviaries should be spacious (minimum 4’ W x 6’ L x 6’ H) to allow movement without risk of escape.
- Provide perches, water baths, and nesting materials to encourage natural behaviors.
4. Behavioral and Physical Rehabilitation
- Gradually increase flight space and encourage exercise to rebuild muscle strength.
- Monitor for signs of stress or illness during rehabilitation, adjusting care as needed.
- Avoid free flying of domestic or recently rescued pigeons to prevent injury or loss.
5. Record Keeping and Identification
- Document leg band information, physical condition, treatments, and progress.
- Use this data to inform release decisions or placement in permanent care.
Practical Tips for Rescuers and Caregivers
- Practice capture techniques using objects before attempting on live birds to ensure quick, safe handling.
- Work in teams when possible to improve safety and efficiency.
- Prepare a bird first aid kit, including saline, antiseptic, gloves, and appropriate medications.
- Educate yourself on avian diseases common in pigeons to recognize symptoms early.
- Network with avian veterinarians and rescue organizations for support and specialized care guidance.
Conclusion
Pigeon rescue and rehabilitation demand a blend of patience, skill, and knowledge. By employing advanced capture methods, providing meticulous initial care, and creating enriching rehabilitation environments, rescuers can significantly enhance recovery rates and welfare outcomes. Continuous learning and collaboration with experts remain essential for advancing rescue success.
This article is intended for experienced rescuers and caregivers aiming to deepen their expertise and improve outcomes for rescued pigeons through proven advanced techniques and best practices.


💬 Comments (0)